- Content:
- What Does It Mean to Be Heterotrophic?
- How Do Fungi Obtain Nutrients?
- How Do Fungi Digest Their Food?
- Importance of Fungi in the Ecosystem
- Conclusion
Fungi are fascinating organisms that play a crucial role in the ecosystem. One of the fundamental questions about fungi is whether they are autotrophic or heterotrophic. Understanding this classification helps us grasp their mode of nutrition and their interactions with other organisms.
What Does It Mean to Be Heterotrophic?
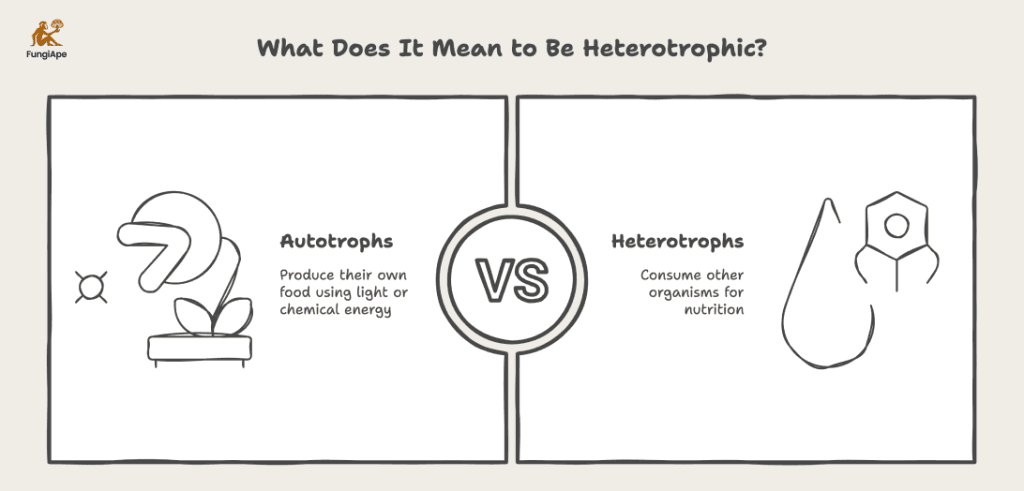
Organisms can be classified into two broad categories based on their mode of nutrition:
- Autotrophs are organisms that produce their own food using light or chemical energy. Plants, algae, and some bacteria fall into this category because they perform photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to generate organic molecules.
- Heterotrophs, on the other hand, rely on consuming other organisms for their nutrition. This category includes animals, fungi, and many bacteria.
How Do Fungi Obtain Nutrients?
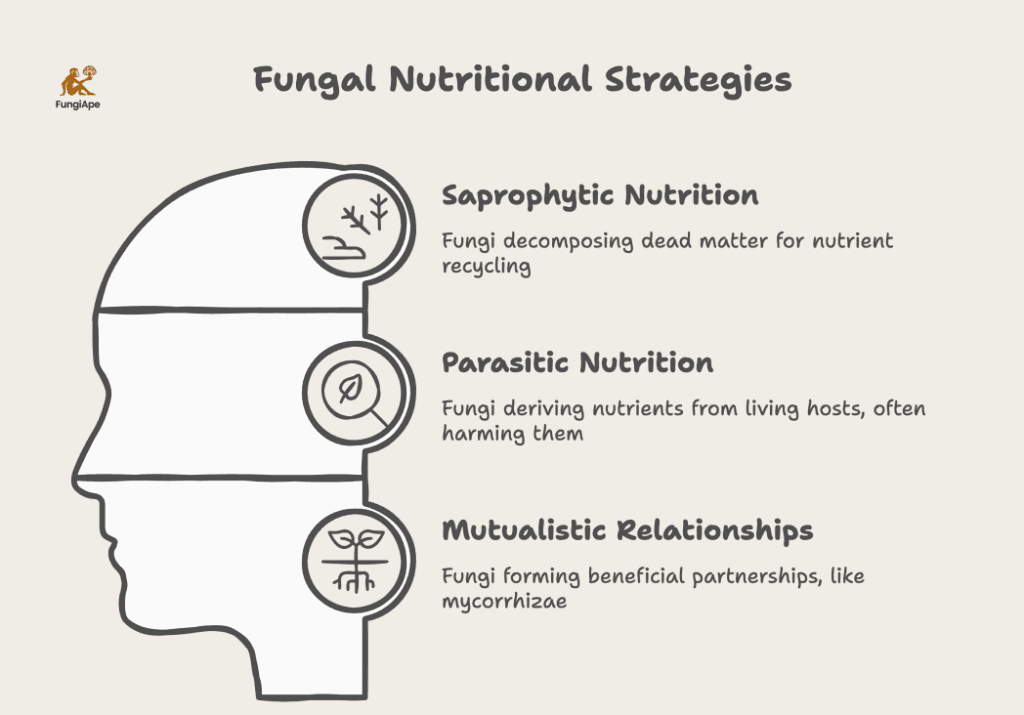
All fungi are heterotrophic, meaning they cannot produce their own food like plants do. Instead, they obtain nutrients by decomposing organic material or forming symbiotic relationships. Here’s how fungi acquire their nutrients:
- Saprophytic Nutrition: Most fungi are decomposers, breaking down dead organic matter. This process is essential for nutrient recycling in ecosystems.
- Parasitic Nutrition: Some fungi live on or inside other organisms, deriving nutrients at the host’s expense.
- Mutualistic Relationships: Certain fungi form beneficial partnerships with other organisms, such as mycorrhizal fungi that enhance plant nutrient absorption.
How Do Fungi Digest Their Food?
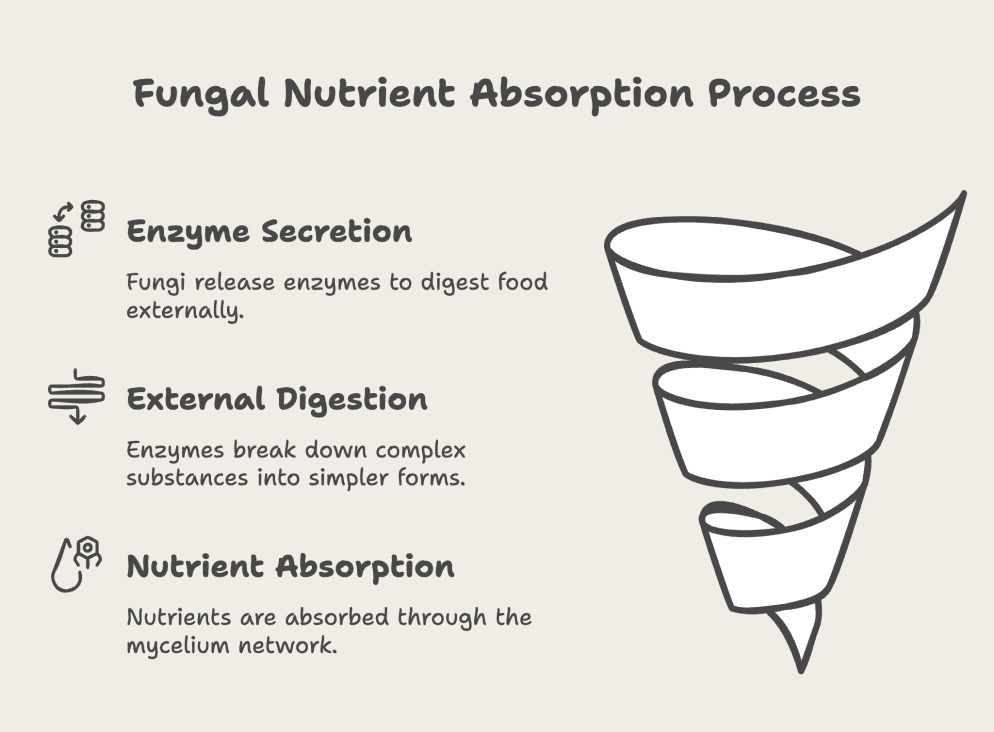
Unlike animals, fungi do not ingest food. Instead, they secrete enzymes onto their food source, breaking it down externally before absorbing the nutrients. This external digestion allows them to decompose complex organic substances efficiently.
Fungi are composed of long, filamentous structures called hyphae, which form an extensive network known as mycelium. This network increases the surface area for absorption, allowing fungi to effectively extract nutrients from their surroundings.
Examples of Heterotrophic Fungi
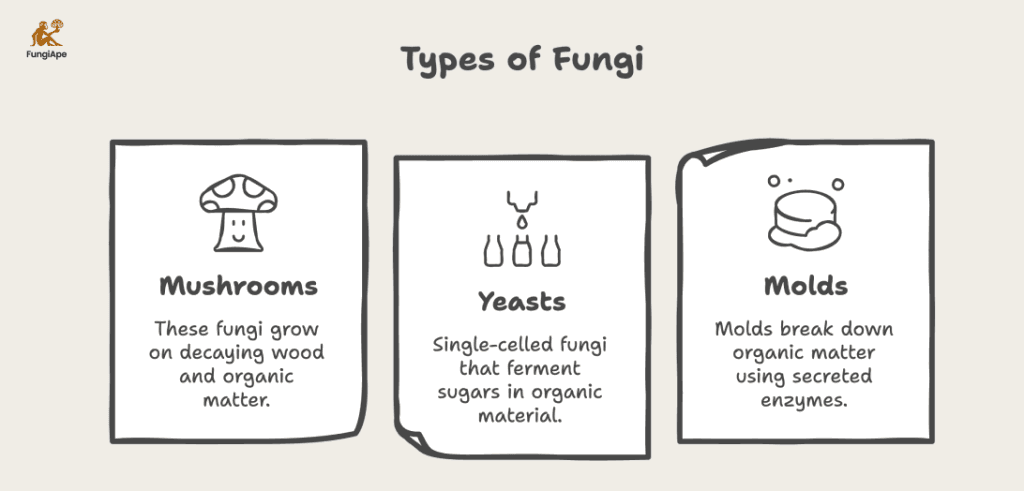
- Mushrooms: These fungi grow on decaying wood and organic matter, breaking it down for nutrients.
- Yeasts: Single-celled fungi that ferment sugars in organic material.
- Molds: Often found on spoiled food, molds break down organic matter using secreted enzymes.
Importance of Fungi in the Ecosystem
Fungi are vital for maintaining ecological balance:
- Decomposers: They recycle nutrients by breaking down dead matter.
- Symbiotic Partners: Mycorrhizal fungi enhance plant growth.
- Medical & Industrial Use: Fungi contribute to antibiotics, food production (e.g., cheese and bread), and bioremediation.
Conclusion
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms that depend on external sources for their nutrients. Their ability to decompose, parasitize, or form symbiotic relationships makes them an essential part of ecosystems. Understanding fungi’s nutritional strategies helps us appreciate their ecological importance and diverse applications in science and industry.
Read more:



